Neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) is a condition experienced by newborn children exposed to opioid prescription or illicit drugs during the prenatal period.
The infant may undergo withdrawal from these substances that manifests as excessive high-pitched crying, irritability, sleep-wake disturbances, alterations in infant tone and movement, feeding difficulties, or gastrointestinal disturbances, usually 1-3 days following birth.
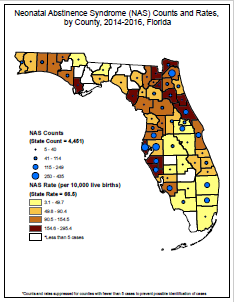
To identify cases, DOH currently uses a passive case ascertainment methodology that relies on linked administrative datasets and diagnostic codes that are indicative of neonatal abstinence syndrome.
Disease Reporting Requirement
All practitioners, health care facilities, and laboratories in Florida are required to notify the Florida Department of Health of diseases or conditions of public health significance under section 381.0031, Florida Statutes, and Chapter 64D-3, Florida Administrative Code.
Process of Identifying NAS Cases
Birth certificate records from the Florida Department of Health’s Bureau of Vital Statistics are linked to the infant’s birth hospitalization record, which is provided as part of quarterly submission of inpatient hospital discharge data by hospitals to the Agency for Health Care Administration (AHCA).
Each discharge record includes International Classification of Diseases’ Clinical Modification diagnosis codes (ICD-10) documented in the hospital.
| ICD-10-CM | P96.1 | drug withdrawal syndrome in infant of dependent mother |
Once an infant’s birth certificate record has been linked to his/her birth hospitalization, the discharge portion of the linked electronic record is scanned for the presence of any of the diagnosis codes.